December 24th, 2025 | Updated on December 30th, 2025
The sales technology landscape has evolved dramatically over the past few years.
Traditional CRM systems and basic automation tools, once considered cutting-edge, now represent just the foundation of a modern sales stack.
A new category of software has emerged to address the growing complexity of B2B sales: AI sales assistant tools.
These platforms differ fundamentally from conventional sales automation software. Rather than simply executing predefined workflows or storing customer data, AI sales assistants actively analyze information, generate insights, and recommend actions in real-time.
They function as intelligent layers that sit alongside existing sales infrastructure, augmenting human capabilities rather than merely automating repetitive tasks.
The distinction matters. Sales teams face mounting pressure to personalize outreach, respond faster to opportunities, and maintain detailed records across dozens of touchpoints—all while hitting aggressive quota targets.
AI sales assistant tools address this challenge by handling cognitive work that traditionally consumed significant rep time: researching prospects, preparing for calls, updating CRM fields, drafting follow-up messages, and identifying next-best actions.
This shift represents a fundamental change in how sales organizations operate. The question is no longer whether to adopt AI-powered tools, but rather which tools solve specific problems for particular sales motions and team structures.
Defining AI Sales Assistant Tools
AI sales assistant tools leverage machine learning, natural language processing, and automation to support sales professionals throughout the customer lifecycle.
Unlike traditional sales enablement platforms that primarily store content or basic automation tools that trigger simple if-then sequences, these systems actively interpret data, generate recommendations, and execute complex tasks with minimal human intervention.
The core capabilities that distinguish true AI sales assistants include:
Contextual intelligence: The ability to analyze multiple data sources—CRM records, email threads, calendar events, call transcripts, web signals—and synthesize relevant insights for specific selling scenarios.
Generative capabilities: Creating original content such as personalized email drafts, meeting summaries, call prep briefs, and CRM updates rather than pulling from static templates.
Adaptive learning: Improving recommendations and outputs based on user feedback, historical patterns, and outcome data across the sales organization.
Proactive assistance: Surfacing insights and suggesting actions without requiring manual queries or navigation through multiple systems.
These characteristics separate AI sales assistants from earlier generations of sales technology. A traditional email automation platform might send sequences on a schedule.
An AI sales assistant analyzes prospect behavior, determines optimal send timing, personalizes messaging based on company intelligence, and adjusts strategy based on engagement patterns—all dynamically.
Key Sales Workflows Supported by AI Assistants
AI sales assistant tools have proven particularly valuable across several critical workflows that historically consumed disproportionate amounts of selling time.
Prospect Research and Account Intelligence
Sales development representatives and account executives spend substantial time researching prospects before initial outreach.
This research phase typically involves reviewing LinkedIn profiles, company websites, recent news, funding announcements, technology stacks, and organizational charts.
Tools like Clay have built entire platforms around enriching prospect data and automating research workflows.
The platform allows sales teams to aggregate information from dozens of data sources, apply AI-powered analysis to identify relevant talking points, and generate personalized outreach angles at scale.
Rather than manually researching each prospect, reps receive pre-compiled intelligence highlighting recent company changes, mutual connections, and relevant industry trends.
Similarly, Aomni specializes in account research for enterprise sales teams. The platform conducts deep research on target accounts, analyzing business priorities, competitive landscape, and potential pain points.
This capability proves particularly valuable for strategic account executives managing complex, multi-stakeholder deals where understanding organizational dynamics determines success.
Artisan takes a different approach by offering AI-powered SDR agents that conduct prospect research autonomously.
These agents identify ideal customer profile matches, research relevant business context, and generate personalized outreach—functioning as virtual team members rather than passive research tools.
Meeting Preparation and Follow-Up
The transition from prospect research to active conversation represents another area where AI assistants provide significant value.
Sales professionals often enter calls with limited context beyond basic CRM notes, forcing them to ask redundant questions or miss opportunities to reference relevant background.
Humanlinker addresses this gap by automatically generating pre-call briefs that synthesize account history, recent interactions, stakeholder information, and suggested conversation topics.
The platform analyzes past meeting notes, email exchanges, and company intelligence to provide actionable context immediately before each call.
Post-meeting workflows present similar challenges. Detailed CRM updates, follow-up emails, and internal summaries require 15-30 minutes after each conversation—time that compounds across dozens of weekly meetings.
Sybill has specialized in solving this specific problem. The platform joins sales calls, transcribes conversations, identifies key moments and action items, generates meeting summaries, and automatically updates CRM fields with relevant information captured during the discussion.
This automation eliminates the manual data entry that sales reps consistently identify as their least favorite task.
Attention offers comparable functionality with additional emphasis on conversation intelligence.
Beyond basic transcription and summarization, the platform analyzes talk patterns, question frequency, objection handling, and deal risk signals.
Sales managers gain visibility into rep performance across all conversations without manually reviewing hours of recordings.
Conversation Intelligence and Coaching
Revenue leaders face a persistent challenge: understanding what happens during the hundreds of sales conversations occurring across their teams each week.
Traditional approaches relied on occasional call reviews and self-reported win/loss analysis, providing limited insight into actual selling behaviors and their correlation with outcomes.
Modern conversation intelligence platforms have transformed this dynamic. Tools like Salesken record, transcribe, and analyze sales calls in real-time, providing immediate feedback on talk time ratios, competitor mentions, pricing discussions, and objection patterns.
The platform identifies specific moments where reps deviated from best practices, enabling targeted coaching rather than generic training.
Oliv AI takes conversation intelligence further by integrating pre-call research, in-call assistance, and post-call automation into a unified workflow.
The platform surfaces relevant information during live calls, suggests responses to common objections, and automatically generates follow-up tasks based on conversation content.
This real-time assistance represents a significant evolution from traditional conversation intelligence. Rather than analyzing calls after the fact, these tools actively support reps during live conversations—functioning more like a knowledgeable colleague than a passive recording system.
Task Automation and Activity Management
Sales professionals juggle dozens of parallel opportunities, each requiring multiple touches across email, phone, social media, and video.
Managing this activity load while maintaining personalization and appropriate timing creates constant prioritization challenges.
Motion addresses this problem through AI-powered task and calendar management.
The platform analyzes a rep’s pipeline, scheduled meetings, task deadlines, and productivity patterns to automatically organize their workday.
Rather than manually prioritizing which prospects to contact when, reps receive intelligent schedules that optimize for deal velocity and quota attainment.
Managr focuses specifically on sales manager workflows, automating routine tasks like pipeline reviews, forecast updates, and team performance analysis.
The platform generates insights about deal health, identifies at-risk opportunities, and surfaces coaching opportunities—allowing managers to focus on strategic guidance rather than data compilation.
For teams seeking simpler automation, Magical provides a lightweight alternative. The tool uses text expansion and workflow automation to eliminate repetitive typing and data entry across any web-based application.
While less sophisticated than specialized sales platforms, Magical offers quick wins for teams hesitant to adopt comprehensive AI systems.
CRM Hygiene and Pipeline Management
Poor CRM data quality undermines virtually every sales operation initiative.
Incomplete records, outdated information, and inconsistent field usage create forecasting errors, inefficient lead routing, and missed opportunities.
Yet sales reps consistently deprioritize CRM updates in favor of actual selling activities.
AI sales assistants have emerged as a practical solution to this chronic problem. Veloxy automatically captures emails, calls, and meetings, then updates CRM records without manual data entry.
The platform uses AI to determine which opportunities should be updated based on activity patterns, ensuring records remain current even when reps forget to log information manually.
Workbounce takes a different approach by functioning as an AI teammate that manages CRM hygiene proactively.
The system monitors data quality issues, prompts reps for missing information at logical moments, and can even update fields autonomously based on email content and call transcripts.
Piper extends this concept by offering an AI sales assistant that manages the entire CRM update workflow through conversational interfaces.
Reps can update opportunities, log activities, and retrieve information using natural language rather than navigating through multiple screens and dropdown menus—dramatically reducing the friction associated with maintaining clean data.
Outbound Campaign Management
Scaling personalized outbound prospecting remains one of sales’ most resource-intensive activities. Traditional approaches required either sacrificing personalization for volume or accepting extremely limited reach to maintain message quality.
Reply.io has built a comprehensive platform combining AI-powered personalization with multi-channel sequencing.
The tool analyzes prospect data to generate customized messaging, manages follow-up cadences across email and LinkedIn, and optimizes send timing based on engagement patterns. Sales teams can maintain high-volume outreach without reverting to generic templates.
Overloop.ai offers similar capabilities with particular emphasis on European markets and GDPR compliance.
The platform automates prospect discovery, enrichment, and multi-touch campaigns while maintaining regulatory compliance—a critical consideration for teams operating across international markets.
Exceed.ai and Conversica both approach outbound automation through AI-powered virtual assistants that conduct two-way email conversations with prospects.
These assistants qualify leads, answer basic questions, and schedule meetings autonomously—functioning as virtual SDRs that operate 24/7 without human intervention.
Core Categories of AI Sales Assistant Tools
The AI sales assistant landscape has evolved into distinct categories, each addressing specific pain points across the sales workflow. Understanding these categories helps teams identify which tools solve their most pressing challenges.
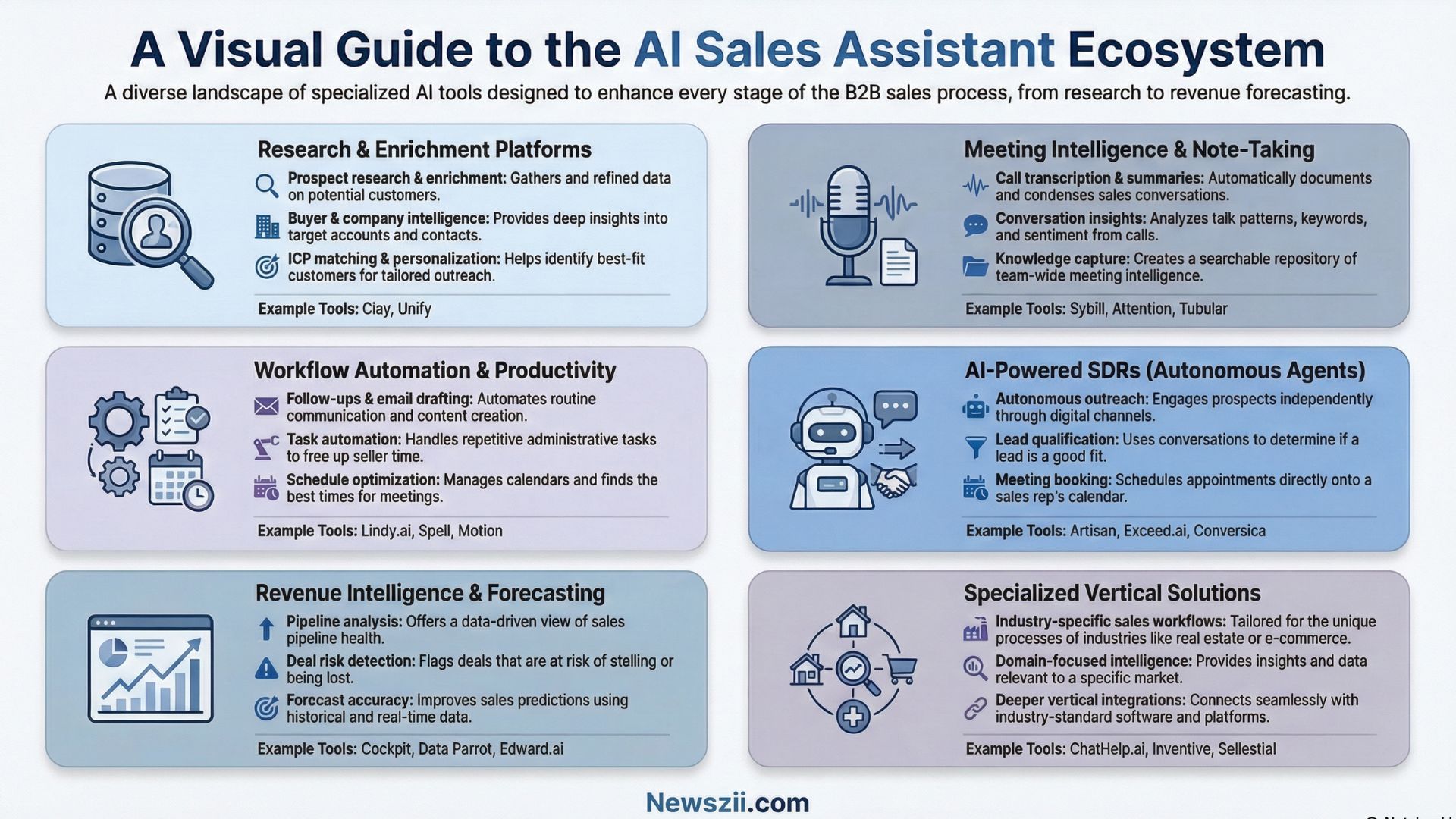
Research and Enrichment Platforms
Platforms focused on prospect intelligence and data enrichment form the foundation of many AI-powered sales operations. These tools automate the manual research that traditionally consumed hours of SDR time.
Clay has established itself as the leading platform in this category. The tool allows users to build custom data enrichment workflows that pull information from dozens of sources, apply AI analysis, and generate actionable insights.
Sales teams use Clay to identify decision-makers, find contact information, research company initiatives, and generate personalized messaging angles—all before initial outreach occurs.
Unify takes a similar approach but emphasizes cross-platform data synthesis. The platform aggregates information from various sales and marketing tools, applies AI to identify patterns and opportunities, and surfaces unified prospect profiles that eliminate the need to toggle between multiple systems.
These enrichment platforms prove particularly valuable for teams running high-volume outbound motions where manual research for each prospect becomes impractical.
The ROI calculation is straightforward: if an SDR can research and personalize outreach for 50 prospects per day instead of 20, the productivity gain directly translates to pipeline generation.
Meeting Intelligence and Note-Taking
Conversation intelligence tools have matured from basic transcription services into sophisticated platforms that extract strategic insights from sales conversations.
Beyond Sybill and Attention mentioned earlier, platforms like Tubular focus specifically on video meeting intelligence.
The tool analyzes not just what was said, but how participants engaged—tracking eye contact, attention levels, and body language cues that indicate interest or concern. For teams selling through video calls, these behavioral signals provide valuable feedback about message resonance.
Zenfetch and Mem.ai approach meeting intelligence from a knowledge management perspective.
Rather than simply storing meeting notes, these platforms build searchable knowledge bases that allow reps to query past conversations, retrieve specific discussions about technical requirements, and identify patterns across multiple customer interactions.
This shift from passive recording to active knowledge synthesis represents a fundamental evolution. Sales teams no longer just archive calls—they build institutional memory that improves with each conversation.
Workflow Automation and Productivity
Tools focused on automating routine sales tasks occupy a distinct category from specialized meeting intelligence or research platforms. These systems aim to eliminate administrative work that prevents reps from actual selling.
Lindy.ai offers customizable AI assistants that handle various workflow automation tasks. Sales teams can configure assistants to manage email triage, schedule meetings, research prospects, or draft follow-ups—essentially building custom solutions for specific pain points without requiring technical expertise.
Spell provides similar flexibility through AI agents that execute multi-step workflows based on natural language instructions.
A sales rep might instruct an agent to “research this company, draft three personalized email variants, and schedule them across the next week”—with the AI handling each step autonomously.
Drafter specializes in one specific but time-consuming task: drafting follow-up emails after sales calls. The platform analyzes call transcripts, identifies action items and key discussion points, then generates contextually appropriate follow-up messages that maintain conversation momentum.
For teams seeking comprehensive productivity solutions, Motion and 1up offer broader calendar and task management capabilities.
These platforms apply AI to optimize daily schedules, prioritize activities based on deal value and urgency, and ensure critical tasks receive appropriate attention.
AI-Powered Sales Development Representatives
Perhaps the most ambitious category involves AI agents that function as autonomous sales representatives rather than simple assistants.
Artisan’s approach of offering AI SDRs that operate independently represents the leading edge of this category.
These agents identify prospects, conduct research, craft outreach, manage responses, and book meetings—handling the entire top-of-funnel workflow with minimal human oversight.
Similarly, Exceed.ai and Conversica deploy AI assistants that engage in multi-turn conversations with prospects. These systems qualify leads through intelligent dialogue, answer questions based on company knowledge bases, and escalate qualified opportunities to human reps only when appropriate.
Pod takes a different approach by positioning itself as an AI-powered sales team rather than individual tools. The platform combines research, outreach, follow-up, and meeting scheduling into an integrated system that operates as a virtual inside sales organization.
The value proposition is compelling: teams can scale prospecting efforts without proportionally scaling headcount. However, this category also faces the highest skepticism.
Prospects often react negatively when they discover they’re communicating with AI rather than humans, and the nuance required for complex B2B sales limits effectiveness in many scenarios.
Revenue Intelligence and Forecasting
While not pure sales assistants, several platforms use AI to analyze pipeline data and improve forecast accuracy—a critical capability for revenue leaders.
Data Parrot focuses specifically on CRM data quality and pipeline analytics. The platform identifies data inconsistencies, predicts deal outcomes based on historical patterns, and flags opportunities requiring attention.
Sales operations teams use these insights to improve forecasting accuracy and identify process gaps.
Cockpit offers real-time revenue intelligence specifically designed for sales managers. The platform analyzes deal progression, identifies stalled opportunities, and recommends interventions based on similar past deals.
This capability transforms reactive pipeline management into proactive deal acceleration.
Edward.ai extends revenue intelligence by analyzing not just CRM data but also email communication, meeting cadence, and stakeholder engagement patterns. The platform uses these signals to predict deal risk and recommend actions that improve win rates.
Specialized Vertical Solutions
Several AI sales assistant tools have emerged targeting specific industries or sales motions that require domain expertise.
ChatHelp.ai focuses on e-commerce and product sales, providing AI-powered chat support that answers product questions, recommends solutions, and guides buyers through purchase decisions. The platform learns from past interactions to improve response quality and conversion rates.
Inventive targets complex technical sales environments where product configuration and solution design represent significant portions of the sales cycle. The platform uses AI to match customer requirements with product capabilities, generate proposals, and ensure technical feasibility before deals advance.
Sellestial specializes in real estate sales, applying AI to property matching, client communication, and transaction management. The vertical focus allows deeper integration with industry-specific systems and workflows that generic sales tools cannot effectively support.
How Modern Sales Teams Implement AI Sales Assistants
The practical implementation of AI sales assistant tools varies significantly based on team structure, sales motion, and organizational maturity. Successful deployments share several common characteristics regardless of specific tool selection.
Small Sales Teams (1-10 Reps)
Smaller teams typically prioritize tools that provide immediate productivity gains without requiring extensive configuration or technical expertise. The focus centers on eliminating the most time-consuming manual tasks rather than building comprehensive AI-powered sales operations.
Tools like Magical, Drafter, and Humanlinker deliver quick wins in this context. A small team can implement basic automation for email drafting, meeting prep, and CRM updates within days rather than weeks.
The learning curve remains minimal, and the tools integrate with existing systems without requiring wholesale process changes.
ChatSpot offers particular value for HubSpot users in this segment. The tool provides a conversational interface for CRM interactions, allowing reps to update records, retrieve information, and trigger workflows using natural language.
For teams already operating within the HubSpot ecosystem, ChatSpot reduces friction without adding another standalone platform.
The common pattern across successful small team implementations: start with one clear pain point, implement a focused solution, measure impact, then expand.
Attempting to deploy comprehensive AI sales assistant stacks simultaneously overwhelms small teams and dilutes adoption.
Mid-Market Sales Teams (10-50 Reps)
Mid-market teams possess sufficient scale to justify more sophisticated tools but often lack dedicated sales operations resources to manage complex implementations.
The sweet spot involves platforms that offer meaningful automation while remaining relatively self-service.
Platforms like Veloxy, Overloop.ai, and Reply.io fit this profile well. These tools provide comprehensive functionality—from prospecting automation to CRM hygiene to pipeline management—within integrated systems that don’t require extensive customization.
Conversation intelligence platforms like Attention and Sybill also prove valuable at this scale. With 10-50 reps conducting hundreds of weekly calls, manual call review becomes impractical.
AI-powered analysis allows sales managers to maintain coaching quality without spending entire days reviewing recordings.
Mid-market teams often layer multiple specialized tools rather than adopting comprehensive platforms.
A typical stack might include Clay for prospect research, Sybill for meeting intelligence, Veloxy for CRM automation, and Reply.io for outbound cadences. The challenge becomes integration management—ensuring these tools share data effectively without creating workflow friction.
Enterprise Sales Teams (50+ Reps)
Large sales organizations approach AI sales assistants differently. These teams typically maintain established sales operations functions, utilize sophisticated CRM configurations, and require enterprise-grade security and compliance features.
Enterprise implementations often begin with conversation intelligence platforms like Attention, Salesken, or Oliv AI.
These tools provide immediate visibility across large, geographically distributed teams while supporting manager development and rep coaching programs. The data generated also informs sales methodology refinement and training content.
Revenue intelligence platforms like Cockpit and Data Parrot become critical at enterprise scale. With hundreds of concurrent opportunities across multiple teams and regions, manual pipeline review proves impossible.
AI-powered analysis identifies patterns, flags risks, and surfaces coaching opportunities that would otherwise remain invisible.
Enterprise teams also invest more heavily in customization and integration.
Rather than using AI sales assistants as standalone tools, they build workflows that connect these platforms with existing systems—marketing automation, customer success platforms, business intelligence tools, and custom internal applications.
Platforms like Glean and Highspot, while not exclusively sales tools, play important roles in enterprise deployments.
These knowledge management platforms use AI to surface relevant content across thousands of documents, ensuring reps access appropriate resources without manual searching.
For organizations with extensive content libraries and complex product portfolios, this capability significantly improves sales effectiveness.
Specialized Sales Motions
Certain sales motions benefit from specific AI assistant capabilities regardless of team size.
Outbound-heavy teams prioritize prospecting automation and research tools. Clay, Artisan, and Reply.io form the core stack, supported by enrichment tools that ensure data quality before outreach begins.
Enterprise sales teams managing complex, multi-stakeholder deals focus on account intelligence and meeting preparation. Humanlinker, Aomni, and conversation intelligence platforms help navigate long sales cycles where relationship quality and strategic positioning determine outcomes.
Product-led growth companies with sales-assist motions need tools that identify expansion opportunities and automate outreach to high-intent users. Platforms like WINN and Fyxer AI specialize in analyzing product usage data to trigger appropriate sales interventions.
Channel sales organizations face unique challenges coordinating partner activities and maintaining visibility across indirect selling motions. While fewer AI sales assistants specifically target channel sales, general-purpose tools like Managr help channel managers track partner performance and identify coaching opportunities.
Selecting the Right AI Sales Assistant Tool
The proliferation of AI sales assistant options creates decision paralysis for many sales leaders. A structured evaluation framework helps identify tools that actually solve specific problems rather than simply following market hype.
Start with Pain Point Identification
Effective tool selection begins with clear problem definition. Sales leaders should audit their teams to identify the specific activities consuming disproportionate time without generating proportional value.
Common high-value targets include:
- Prospect research before outreach (2-3 hours daily per SDR)
- CRM data entry and updates (1-2 hours daily per rep)
- Meeting preparation and follow-up (30-45 minutes per meeting)
- Email drafting and personalization (45-60 minutes daily)
- Pipeline reviews and deal analysis (3-5 hours weekly for managers)
Quantifying time spent on each activity provides objective data for ROI calculations. If SDRs spend 2.5 hours daily on prospect research, and a tool like Clay reduces this to 45 minutes, the productivity gain directly impacts pipeline generation capacity.
Evaluate Integration Requirements
AI sales assistants deliver maximum value when they seamlessly integrate with existing systems. Tools that require manual data transfer or operate in isolation create friction that undermines adoption.
Critical integration points include:
- CRM platform (Salesforce, HubSpot, Pipedrive, etc.)
- Email system (Gmail, Outlook)
- Calendar application
- Communication platforms (Slack, Teams)
- Existing conversation intelligence or enablement tools
Some platforms offer native integrations with major systems, while others rely on middleware like Zapier. Native integrations typically provide richer functionality and better reliability, though middleware solutions offer flexibility for custom workflows.
Teams should also consider data flow requirements. Does information need to flow bidirectionally between systems? Can the tool write data back to the CRM automatically, or does it require manual syncing? These technical details significantly impact practical utility.
Assess Learning Curve and Change Management
Even highly effective tools fail if sales teams don’t adopt them. The implementation timeline, training requirements, and behavioral changes required all influence success rates.
Tools like Magical and ChatSpot require minimal training—reps can begin using them productively within minutes. Comprehensive platforms like Clay or advanced conversation intelligence systems require more substantial onboarding, potentially including formal training sessions and ongoing support.
Sales leaders should evaluate:
- How long before reps become proficient?
- Does the tool integrate into existing workflows or require new processes?
- What ongoing maintenance and optimization does the platform need?
- Who owns implementation and adoption within the organization?
Teams without dedicated sales operations resources should favor tools with lower implementation complexity. Conversely, organizations with strong RevOps capabilities can successfully deploy more sophisticated platforms that require configuration and ongoing optimization.
Consider Total Cost of Ownership
AI sales assistant pricing varies dramatically—from $10 per user monthly for basic tools to several hundred dollars per seat for comprehensive platforms. However, the sticker price represents only part of total cost.
Additional cost factors include:
- Implementation and configuration time
- Training and onboarding resources
- Integration development or middleware costs
- Ongoing optimization and management
- Data enrichment or API usage fees (common with research platforms)
Some platforms charge based on usage rather than seats. Tools that consume external data sources, run AI models, or process large volumes of conversations often implement consumption-based pricing. Teams should model expected usage to avoid budget surprises.
The ROI calculation should account for both time savings and quality improvements. If conversation intelligence improves win rates by 5% while also saving managers 4 hours weekly, both benefits contribute to total value.
Evaluate Vendor Maturity and Roadmap
The AI sales assistant market remains relatively young, with many vendors operating for less than three years. Vendor stability matters—particularly when tools become embedded in critical sales workflows.
Evaluation criteria include:
- Funding status and runway
- Customer base size and composition
- Product update frequency and feature velocity
- Support quality and responsiveness
- Data security and compliance certifications
Sales leaders should also understand product direction. Does the vendor plan to remain focused on their core capability, or are they expanding into adjacent categories? Feature sprawl can dilute product quality, while too-narrow focus might miss evolving needs.
Reference calls with existing customers provide valuable insights beyond marketing materials. How does the tool perform under actual use conditions? What unexpected challenges emerged during implementation? Would they choose the same tool again?
Implementation Challenges and Limitations
Despite significant capabilities, AI sales assistant tools face practical limitations that organizations must navigate. Understanding these constraints helps set appropriate expectations and avoid common pitfalls.
Data Quality Dependencies
AI sales assistants generate value by analyzing existing data and patterns. When underlying data is sparse, inconsistent, or inaccurate, outputs suffer accordingly.
Conversation intelligence platforms require consistent call recording to identify patterns.
Research tools need accurate firmographic data to generate relevant insights. Forecasting systems depend on complete pipeline data to predict outcomes reliably.
Teams with poor CRM hygiene often discover that AI tools exacerbate existing data problems rather than solving them.
Garbage in, garbage out applies directly—perhaps more so than with traditional software because AI systems make the consequences of bad data more visible.
Addressing this limitation requires parallel focus on data quality improvement. Implementing an AI sales assistant provides motivation to clean up existing data, but organizations should anticipate an initial period where outputs remain inconsistent while data quality improves.
Personalization Versus Scale Tensions
Many AI sales assistants promise both high personalization and massive scale. In practice, this combination proves difficult to achieve. Truly personalized outreach requires deep research and thoughtful customization—activities that inherently limit volume.
Tools that prioritize volume typically sacrifice some personalization depth. Platforms generating hundreds of daily emails per SDR rely on templates with variable insertion rather than fully custom messaging.
This approach works for certain sales motions but falls short when targeting senior executives or complex accounts requiring strategic positioning.
Sales leaders must consciously choose where they fall on the personalization-scale spectrum.
Outbound motions targeting mid-market accounts with clear personas can effectively leverage high-volume, moderately personalized approaches. Enterprise sales require deeper personalization, limiting practical scale regardless of tool capabilities.
AI Accuracy and Hallucination Risks
Large language models powering many AI sales assistants occasionally generate plausible-sounding but inaccurate information—commonly termed “hallucinations.” This risk proves particularly problematic in sales contexts where factual errors damage credibility.
Meeting summaries might misattribute statements or incorrectly capture action items. Research tools might confidently present outdated information about prospects.
Email drafts might include claims about product capabilities that don’t exist.
Responsible implementations include human review checkpoints before AI-generated content reaches customers. Automatically generated emails should require approval before sending.
Meeting summaries should be verified before sharing with prospects. Research briefs should clearly indicate information sources and confidence levels.
Some platforms provide transparency features that help users assess output reliability. Citation links, confidence scores, and source attribution allow sales reps to verify AI-generated information before relying on it.
Compliance and Privacy Considerations
AI sales assistants that process customer conversations, email content, or personal information raise compliance questions—particularly in regulated industries or when operating across international markets.
Conversation intelligence platforms recording customer calls must comply with consent requirements that vary by jurisdiction.
Some regions require two-party consent for call recording; others permit recording with simple notification. GDPR adds additional constraints on processing and storing personal data.
Organizations must evaluate:
- Where is customer data stored and processed?
- What data residency requirements apply?
- How long is data retained?
- Can data be deleted upon customer request?
- What security certifications does the vendor maintain?
Enterprise buyers typically require SOC 2 certification, GDPR compliance documentation, and security questionnaire completion before approving purchases. Smaller vendors may lack these certifications, limiting viability for large organizations or regulated industries.
Behavioral Adoption Challenges
Sales reps resist tools that create additional work without clear benefit. If an AI sales assistant requires manual setup, regular maintenance, or generates outputs that still need substantial editing, adoption falters.
Successful implementations minimize friction by:
- Integrating directly into existing workflows rather than requiring new processes
- Delivering value from initial use rather than requiring extensive configuration
- Producing outputs that reps actually use rather than ignore
- Requiring minimal ongoing maintenance
Tools that passively capture data (conversation intelligence platforms) typically achieve higher adoption than those requiring active input (prospecting research tools where reps must manually trigger analysis).
Sales leadership significantly influences adoption through consistent messaging about expectations and accountability.
If managers don’t regularly reference AI-generated insights during coaching sessions or pipeline reviews, reps quickly perceive the tool as optional.
The Evolving Role of AI in Sales Organizations
AI sales assistant tools have matured rapidly over the past three years, but the category remains in relatively early stages. Several trends will likely shape the next phase of evolution.
From Point Solutions to Integrated Platforms
The current landscape features dozens of specialized tools, each solving specific pain points. This fragmentation creates integration challenges and cognitive overhead as reps navigate multiple interfaces.
Market consolidation appears inevitable. Larger platforms will absorb point solution functionality, while some specialized vendors will expand into adjacent categories.
The ultimate goal: comprehensive AI sales assistant platforms that support entire workflows within unified interfaces.
Early signs of this consolidation already exist. CRM vendors increasingly incorporate AI capabilities previously available only through third-party tools.
Salesforce’s Einstein and HubSpot’s AI features now include conversation intelligence, email generation, and pipeline analysis—functionality that required separate purchases previously.
Independent vendors respond by going deeper in their specializations or by building comprehensive platforms themselves.
The middle ground—decent capabilities across multiple categories without excellence in any—becomes increasingly difficult to defend.
Autonomous Agents Handling More Complex Work
Current AI sales assistants primarily support human reps rather than replacing them. The next generation will likely handle increasingly sophisticated tasks autonomously.
Early autonomous agents like those from Artisan, Exceed.ai, and Conversica currently focus on relatively simple tasks: initial outreach, basic qualification, meeting scheduling.
These activities involve limited decision-making and can be managed through structured workflows.
Advances in language models and reasoning capabilities will enable autonomous handling of more complex scenarios.
AI agents might soon conduct discovery calls, navigate multi-stakeholder conversations, and negotiate within defined parameters—not just schedule meetings but actually progress opportunities through pipeline stages.
This evolution raises important questions about sales organizational structure. If AI agents can effectively handle initial qualification and discovery, how does that reshape SDR and AE roles? What work remains exclusively in human domains, and how do teams develop those skills?
Deeper Behavioral Intelligence and Coaching
Conversation intelligence platforms currently analyze what was said during sales calls. Future systems will provide much deeper insight into how those conversations unfolded and why certain approaches succeeded or failed.
Advanced behavioral analysis might evaluate:
- Emotional resonance and rapport-building effectiveness
- Question sequencing and discovery depth
- Objection handling sophistication
- Stakeholder influence mapping across multi-party calls
- Competitive positioning and differentiation quality
This analysis could power personalized coaching that adapts to individual rep development needs rather than generic training programs.
AI coaches might identify specific skill gaps, recommend targeted improvement activities, and provide real-time feedback during live calls.
Platforms like Tubular already analyze video engagement signals. Expanding this capability to assess communication effectiveness, message clarity, and persuasion techniques represents a natural evolution.
Revenue Intelligence Becoming Predictive
Current revenue intelligence tools primarily analyze historical patterns and current pipeline health. Future systems will likely offer more sophisticated predictive capabilities that improve strategic decision-making.
Advanced AI might predict:
- Optimal pricing strategies for specific deals based on buyer signals
- Most effective stakeholder engagement sequences for complex opportunities
- Likelihood of competitive displacement in existing accounts
- Resource allocation recommendations to maximize revenue outcomes
- Market opportunity identification based on win pattern analysis
These capabilities would shift AI sales assistants from tactical execution support toward strategic planning tools that inform territory design, compensation structure, and go-to-market strategy.
Multimodal AI Creating Richer Experiences
Most current AI sales assistants process text and audio. Future systems will likely incorporate visual analysis, video generation, and interactive demonstration capabilities.
Multimodal AI might:
- Analyze prospect body language during video calls to assess engagement
- Generate personalized product demo videos automatically
- Create custom visualizations explaining complex concepts
- Produce interactive ROI calculators tailored to specific prospects
- Develop proposal presentations that adapt based on viewing behavior
This evolution could dramatically improve personalization quality while maintaining scale—addressing one of the core tensions in current implementations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are AI sales assistant tools?
AI sales assistant tools are software platforms that use artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing to support sales professionals throughout the customer lifecycle.
Unlike traditional sales automation that executes predefined workflows, these tools actively analyze data, generate insights, create content, and recommend actions in real-time.
They handle cognitive work such as prospect research, meeting preparation, CRM updates, and follow-up communication—augmenting human capabilities rather than simply automating repetitive tasks.
How do AI sales assistants help sales teams?
AI sales assistants provide value across multiple dimensions. They save time by automating research, data entry, and administrative work that typically consumes 30-40% of a sales rep’s day.
They improve quality by generating personalized outreach, identifying relevant talking points, and surfacing account intelligence that humans might miss.
They enhance consistency by ensuring every prospect receives appropriate follow-up and every opportunity maintains complete records.
They also provide visibility by analyzing patterns across hundreds of conversations, enabling better coaching and forecasting.
Are AI sales assistants suitable for small sales teams?
Small sales teams can benefit significantly from AI sales assistants, though tool selection matters.
Platforms requiring extensive configuration, technical integration, or dedicated administration often prove impractical for teams lacking sales operations resources. However, simpler tools focused on specific pain points—email drafting, meeting summarization, basic CRM automation—deliver immediate value without implementation complexity.
Small teams should prioritize tools with low learning curves, minimal integration requirements, and clear ROI on the most time-consuming manual tasks.
How are AI sales assistants different from CRM tools?
CRM platforms primarily store customer data, manage pipeline stages, and provide reporting on sales activities.
They serve as systems of record but require manual data entry and offer limited intelligence about what actions to take.
AI sales assistants layer on top of CRMs, automatically capturing information from conversations and emails, analyzing patterns to surface insights, and recommending specific next steps for individual opportunities.
While CRMs answer “what happened,” AI sales assistants address “what should happen next” and increasingly execute those actions autonomously.
Can AI sales assistants replace human sales reps?
Current AI sales assistant technology cannot fully replace human sales professionals, particularly in complex B2B environments requiring strategic thinking, relationship building, and nuanced problem-solving.
However, AI agents are increasingly capable of handling structured, early-stage activities like prospecting, qualification, and meeting scheduling.
The more likely scenario involves AI handling transactional elements while humans focus on consultative selling, strategic account management, and relationship development. Sales roles will evolve to emphasize uniquely human capabilities as AI assumes routine tasks.
How should businesses choose the right AI sales assistant tool?
Effective tool selection begins with identifying specific pain points consuming disproportionate time without generating value.
Organizations should quantify time spent on activities like prospect research, CRM updates, meeting prep, and email composition, then evaluate tools addressing the highest-impact areas.
Integration capabilities with existing systems, implementation complexity, total cost of ownership, and vendor stability all influence selection.
Teams should start with focused solutions addressing clear problems rather than attempting comprehensive platform deployments simultaneously. Pilot programs with small user groups help validate effectiveness before broader rollout.
Conclusion
AI sales assistant tools have transitioned from experimental technology to practical business systems that measurably impact sales productivity and effectiveness.
The category encompasses diverse platforms—from research automation to conversation intelligence to autonomous prospecting agents—each addressing specific challenges that sales teams face.
The most successful implementations share common characteristics: clear problem identification, appropriate tool selection for organizational maturity, thoughtful change management, and realistic expectations about capabilities and limitations.
Organizations that approach adoption strategically see substantial returns through time savings, quality improvements, and enhanced visibility into sales activities.
The technology continues evolving rapidly. What current tools handle with human oversight, future systems may manage autonomously.
The fundamental value proposition remains constant: enabling sales professionals to focus on high-judgment activities that drive revenue while AI handles routine cognitive work.
For sales leaders evaluating options, the decision is no longer whether to adopt AI sales assistants but rather which capabilities to implement first and how to structure deployment for maximum impact.
The tools exist, the technology works, and competitive dynamics increasingly favor organizations that effectively augment human sales teams with artificial intelligence.
The question facing revenue organizations today centers on execution: how quickly can they identify high-value use cases, select appropriate tools, drive adoption, and capture the productivity gains that AI sales assistants make possible?
Those who answer this question effectively will maintain distinct competitive advantages as AI capabilities continue advancing and expectations for sales efficiency continue rising.